Transient Insomnia: What It Is and Why It’s Unique
Insomnia is a term that encompasses a wide range of sleep conditions and includes trouble falling and staying asleep and waking frequently during the night. Almost 70% of adults report getting insufficient sleep at least one night per month, while 11% suffer almost every night.

The latter of these two scenarios is an example of recurring, or chronic, insomnia that plagues sufferers for months, years, or even their entire life. Acute insomnia, (also known as transient insomnia) on the other hand, is a short-term condition and may come and go with time. This type of insomnia is usually caused by a specific event or situation.
Here we’ll take a closer look at exactly what transient insomnia is, including side effects, symptoms, and treatment options.
Content
Transient Insomnia vs. Chronic Insomnia
To put it simply, transient insomnia describes trouble sleeping for three months or less. Chronic insomnia occurs when someone has difficulty falling or staying asleep for more than three consecutive months.

While transient acute insomnia can last from several days to a few weeks, it’s usually triggered by a particular event or underlying condition. Chronic insomnia, on the other hand, persists for months at a time with no definitive cause.
Signs and Symptoms of Transient Insomnia
Diagnosing transient insomnia can be difficult since it occurs for such a short period of time. It’s hard to tell the difference between acute insomnia that only lasts a few days and simply having a bad night’s sleep.

Here are some of the most obvious symptoms of transient insomnia to make diagnosing this condition a bit easier:
- Trouble falling asleep
- Difficulty falling back to sleep once awake
- Trouble staying asleep
- Poor sleep quality
- Inability to focus or function during the daytime due to inadequate sleep
Symptoms of transient insomnia can occur at any time, either during the night, before trying to go to sleep, or in the early morning hours. These three periods of time are called onset, maintenance, and late insomnia. Regardless of when transient insomnia hits, many of the side-effects are the same and include:
- Feeling tired and disoriented upon waking up
- Mood swings and irritability
- Difficulty focusing
- Memory impairment
- Feeling clumsy or uncoordinated
- Reduced work performance and frequent errors
- Trouble socializing or engaging in conversation
Many people will experience a combination of these symptoms when battling transient insomnia.
Common Causes of Transient Insomnia
So, what exactly causes these short periods of restless and interrupted sleep? Most triggers are psychological lifestyle factors that include:

- Stress/Anxiety
- Depression
- Grief
- Chronic pain
- Alcohol or drug abuse
- Certain medications
- Traumatic events
- Significant life changes (death, divorce, a move)
- Unusual events
- Sleeping in a new place
- Changes in diet or eating the wrong foods before bed
- Caffeine intake
- Daylight savings time
- Jetlag
Any of these triggers can cause a disruption in your normal sleep patterns, making it difficult to fall and stay asleep.
Stress, Anxiety, and Depression
Stress, anxiety, and depression all lead to racing thoughts. The more tense your body is, the harder it is for you to relax and fall asleep. This is one reason muscle relaxing techniques are used to help treat insomnia. Stress and anxiety also keep many people in a state of alertness, making it difficult to fall asleep. Rapid, anxious thoughts often occur at night when you’re not moving and your mind is free to wander. Lack of sleep or the inability to fall asleep can cause even more stress, creating a vicious cycle of transient insomnia.
Similar to stress, grief, traumatic events, or major life changes also make it difficult to quiet your mind and relax enough to fall and stay asleep.
Sleeping in New Environments
Sleeping in a new or unusual place can cause transient insomnia due to our body’s natural instinct to protect us. Your brain automatically senses potential danger or harm in a new environment. Even if you consciously know that you’re perfectly safe, your brain is on heightened awareness. In an effort to keep you safe, your brain will make it difficult for you to fall and stay asleep in unfamiliar surroundings.
Illegal Drug Use and Alcohol Consumption
Transient insomnia is connected to a wide range of both illegal and prescription substances, as well as alcohol. Anytime you ingest illegal drugs or alcohol, you’re interfering with your body’s natural ability to function — this includes falling and staying asleep at night. Alcohol interferes with your brain’s production of adenosine, a sleep-inducing chemical. While it actually increases production while you’re actively consuming alcohol, making it easier for you to fall asleep, as the chemical quickly dissipates, you’re more likely to wake up throughout the night.
Drugs affect your sleep in a number of ways — both legal and illegal. Substances like cocaine and methamphetamine increase your brain’s production of dopamine — a chemical associated with feelings of happiness and relaxation. While, at first, it might sound like these drugs would make you tired, over time, they can cause sleep deprivation by interfering with your brain’s dopamine receptors.
Medications
The side effects of certain prescription and over-the-counter medications can also cause transient insomnia. Some of the most common include:
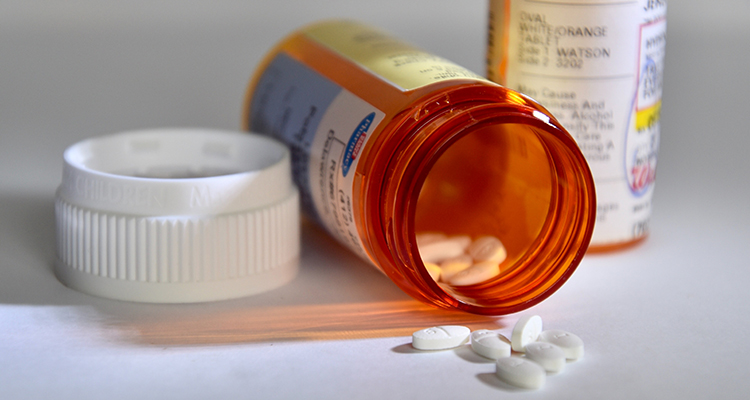
- Alpha- and beta-blockers
- Steroids
- Antidepressants
- ACE inhibitors
- Statins
- Second-generation H-1 antagonists
- Cholinesterase inhibitors
Each of these medications, and many others, can interfere with your REM sleep, cause nightmares, and increased alertness.
Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is a common cause of long-term insomnia, but it can also cause transient insomnia when it’s the result of a recent injury or short-term impairment. Pain makes it difficult to find a comfortable sleeping position. It can also increase stress levels and cause depression. Drug use is another risk associated with chronic pain. In an effort to ease pain, some people become dependent or even addicted to painkillers — both prescription and over-the-counter — which can lead to an entirely new host of problems and causes of transient insomnia.
Consuming Certain Foods and Drink Before Bed
Consuming caffeine before bed is never a good idea. Coffee, tea, or other beverages that contain caffeine can make it nearly impossible to fall asleep. After all, most people consume these beverages in the morning or throughout the day for a boost in energy. That’s because caffeine blocks adenosine receptors in the brain. During the day, your levels of adenosine slowly increase. As they build up, you become more tired, preparing you for sleep at night. Caffeine blocks these levels from building, keeping you awake longer.
It’s not just the things we drink, but also the foods we eat that can cause transient insomnia. Consuming large meals or foods high in fat and sugar before bed triggers your body to produce insulin. Insulin is linked to your body’s natural circadian rhythm (or sleep-wake cycle). Food triggers your brain that it should be awake. Your body may also struggle to digest large meals before bed, causing discomfort and difficulty getting comfortable. You may also find yourself waking more frequently with gas, bloating, or heartburn. According to some experts, your last meal should be 3 hours before going to bed to give your body ample time to digest and prepare for sleep.
Daylight Savings Time and Jet Lag
These are infrequent occurrences that can potentially cause transient insomnia in some people. Your body’s circadian rhythm (sleep-wake cycle) is based on your normal, natural sleep patterns. People generally tend to go to sleep and wake around the same time each day. As night falls, you begin to prepare both physically and mentally for sleep. In the morning, you wake up to your alarm and perform your daily tasks. This creates a very specific routine inside your body that your brain becomes accustomed to. When something interferes with this routine, it affects your circadian rhythm and your body’s ability to know the difference between when it should be awake and when it should be resting.

Daylight savings time isn’t observed everywhere, but where it is, even just an hour difference in time can significantly impact your sleep patterns. When you “spring ahead”, the mornings are much darker and it stays light much later at night. This inconsistency from what you’re used to can trick your brain into thinking you should be awake when really you should be sleeping. It generally takes a week or two for your circadian rhythm to readjust to this new schedule.
Treating and Preventing Transient Insomnia
Sometimes, insomnia just happens. Unexpected major life events, stress, or travel can all affect your body’s internal clock and your ability to fall and stay asleep. While you can’t always prevent transient insomnia, you can take certain measures to help prevent it or lessen its effects.

Practice Mindfulness and Meditation
Reducing stress and anxiety is one way to prevent transient insomnia. With nearly 80% of adults claiming to be stressed, these feelings can make it nearly impossible to achieve a quality night’s sleep. Even just a few moments of meditation or mindfulness each day can significantly reduce stress levels, preventing you from getting overwhelmed or consumed by your thoughts. You can also tap into these techniques if you’re faced with a traumatic event or major lifestyle change. Yoga is another great way to reduce stress and improve sleep.
Room Darkening Shades
If time changes affect your sleep, room darkening shades might help. In some parts of the country, daylight savings time can cause it to stay light until almost 9:00 at night! If this is messing with your circadian rhythm, try room darkening shades in your bedroom. This way, you can trick your mind and body into thinking it’s dark out and time for sleep.
Avoid Large Meals and Caffeine
This is an easy fix for preventing transient insomnia. Avoid drinking caffeinated drinks or eating large meals too close to bedtime. If possible, eat your last meal 2 to 3 hours before bed to prevent insulin production and discomfort.
Holistic Healing
If possible, avoid taking prescription or over-the-counter medications. Of course, there are some medical conditions and illnesses that require specific medication and can’t be avoided. But whenever possible, opt for holistic approaches like acupuncture, chiropractic care, naturopathy, or homeopathy. Treating certain conditions naturally can eliminate the need for harmful medications or dependencies that may cause transient insomnia.
Adopt a Healthy Sleep Routine
Not only can establishing a healthy sleep routine help prevent transient insomnia, but it can improve your overall health and wellbeing. Whenever possible, stick to the same sleep schedule, regardless of where you are. Try to go to bed and wake up around the same time each day. Perform the same nightly rituals before bed. This may include writing in your journal, meditating, reading a book, or drinking soothing chamomile tea. Avoid screens like your phone, TV, or tablet at least 60 minutes before bed. The blue light from these devices can interfere with your brain’s natural melatonin production. The best part about adopting healthy sleep habits is that you can carry most of these wherever you go, helping ward off transient insomnia when traveling or sleeping in new and unfamiliar environments.
Understanding and Avoiding Transient Insomnia
Now you have a better understanding of exactly what transient insomnia is, including its causes and ways to prevent it from impacting your life. Sadly, the stress, responsibility, and unpredictability of everyday life lend themselves to unwanted bouts of transient insomnia. The good news is, with the right resources and techniques, you can prevent sleepless nights and embrace longer, deeper sleep.

Somnus Therapy can help you embrace quality sleep that leaves you feeling energized, refreshed, and enlightened. Using CBT techniques, mindfulness, cognitive restructuring, and sleep restriction therapy, we offer a comprehensive approach to overcoming insomnia so you can achieve blissful sleep. Start your journey today!